Linking JavaScript file and html file
Adding JavaScript into an HTML Document
You can add JavaScript code in an HTML document by employing the dedicated HTML tag<script> that wraps around JavaScript code.
The <script> tag can be placed in the <head> section of your HTML, in the <body> section, or after the </body> close tag, depending on when you want the JavaScript to load.
Method 1: Inline Mode
不便于代码分离
Method 2: using <script> tag
The <script> tag can be placed in the <head> section of your HTML, in the <body> section, or after the </body> close tag, depending on when you want the JavaScript to load.
- Internal Style
- External Style
浏览器先执行完
<script>tag才会渲染其他组件
JavaScript Fundamentals
variables
- three ways of variable declaration:
- let
- var
- const
We use those three keywords to create variables in JavaScript. Example: let message; or var message; or const message;
- var variables are defined from the beginning of the function, no matter where the definition is.
- var has no block scope.
- var can be declared many times, but let and const cannot in the same scope.
- const is used to declare a constant (unchanging) variable(immutable)
- let has only block scope, while var can be global
Data Types
JavaScript is “dynamically typed”, meaning that there are data types, but variables are not bound to any of them.
Date types: Number, String, Boolean, Object, Function, Null, Undefined
Number- The number type serves both for integer and floating point numbers: 123, 12.22..Note:
NaNbelong to the type number but it’s not “normal” numbers.NaNrepresents an error.String- A string may consist of only one character or many of them. Double and single quotes have no difference between them in JavaScript. E.g. ‘aba’, “I am a string.”Boolean- The boolean type has only two values: true and false.Null- A special value which is for unknown values.In JavaScript null is not a “reference to a non-existing object” or a “null pointer” like in some other languages.
It’s just a special value which has the sense of “nothing”, “empty” or “value unknown”.Example:
var age = null;
The code above states that the age is unknown or empty for some reason.Undefined- A special value which is for unassigned values. The meaning of undefined is “value is not assigned”.
Undefined 和 null 不是数据类型,而是特殊值
- Function and Object will cover on the following section.
typeof Operator
returns the type of the argument. It’s useful when we want to process values of different types differently, or just want to make a quick check.
e.g. typeof “abc” - string
Comparisons
A comparison returns a value. The value is of the boolean type: true or false.
- Greater/less than:
a > b,a < b. - Greater/less than or equals:
a >= b,a <= b. - Equality check is written as
a == b(please note the double equation sign=. A single symbola = bwould mean an assignment). - Not equals. In maths the notation is
≠, in JavaScript it’s written as an assignment with an exclamation sign before it:a != b.
Note:
A regular equality check == has a problem. It cannot differ 0 from false:
1 | 0 == false // true |
That’s because operands of different types are converted to a number by the equality operator ==. An empty string, just like false, becomes a zero.1
Number(false) => 0, Number(“”) => 0
What to do if we’d like to differentiate 0 from false?
A strict equality operator === checks the equality without type conversion.
In other words, if a and b are of different types, then a===b immediately returns false without an attempt to convert them.
1 | 0 === false // false |
Function
Functions are the main “building blocks” of the program. They allow the code to be called many times without repetition.
- Function Declaration
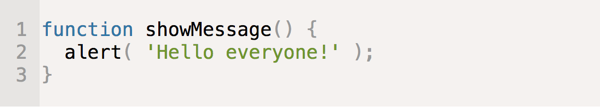
The function keyword goes first, then goes the name of the function, then a list of parameters between the parentheses (empty in the example above) and finally the code of the function, also named “the function body”, between curly braces.
- Function Expression

The meaning of these code samples is the same: “create a function and put it into the variable sayHi”.
Object
- Objects are used to store keyed collections of various data and more complex entities.
e.g. Dog object: age, name, color, breed attributes, and run() activity.
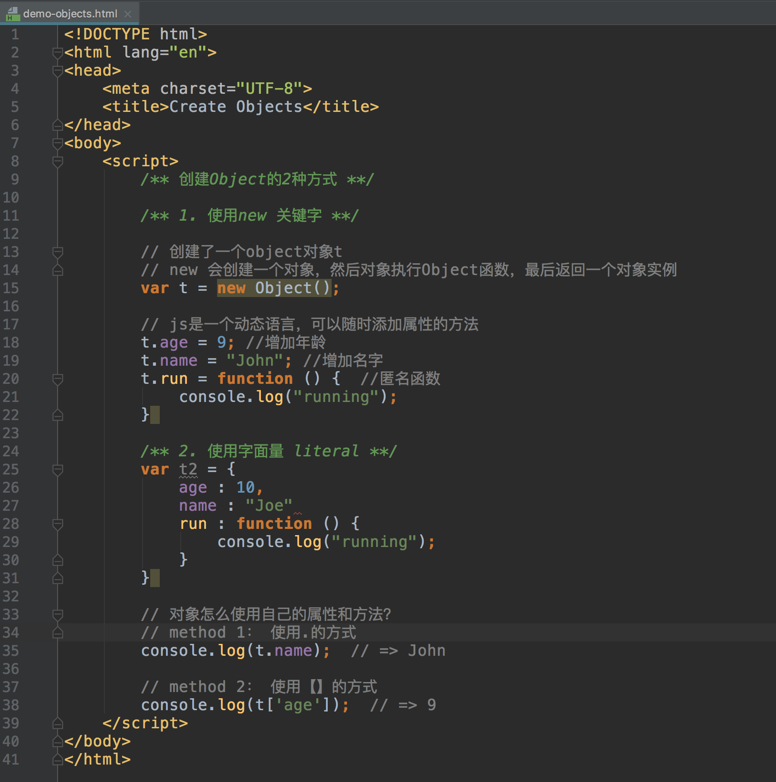
How to create an instance of object
using new keyword
E.g.
1
2
3var car = new Car();
car.color = “red”;
car.type = “suv”;using literal {} 字面量
E.g.var car = { color: ‘red’, type: ‘suv’};
Use
.or[]to visit attributes.eg
1
2
3t2.name;
t2['age'];
t2['run'](); // function callexample
Primitive Type VS. Reference Type
- Numbers, Strings, Booleans, and the null and undefined types are primitive.
- Objects, and functions are reference types.
Difference:
A primitive type has a fixed size in memory. For example, a number occupies eight bytes of memory, and a boolean value can be represented with only one bit. A reference type does not have a fixed size in memory.
Primitive types are assigned/copied “as a whole value”, but reference types are stored and copied “by reference”.
A variable stores not the object itself, but its “address in memory”, in other words “a reference” to it.
When an object variable is copied.the reference is copied, the object is not duplicated.
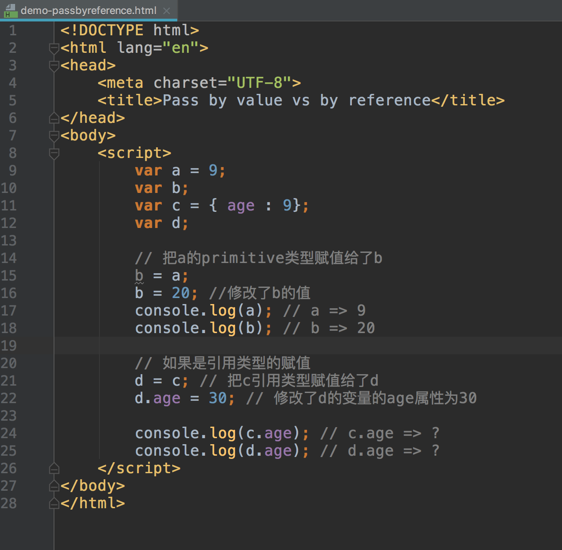
Pass by reference and pass by value
- In JavaScript primitive types are copied and passed by value and objects are copied and passed by reference value.
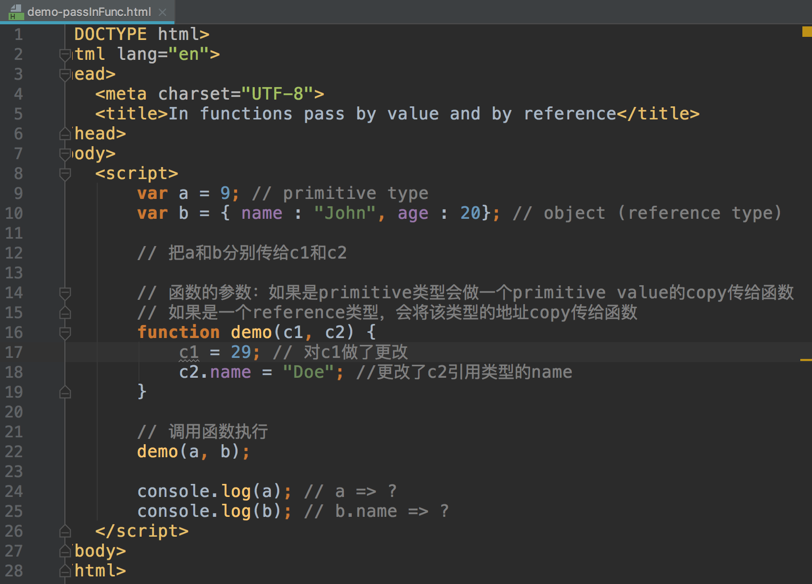
In terms of function:
In Pass by Value, function is called by directly passing the value of the variable as the argument. Changing the argument inside the function doesn’t affect the variable passed from outside the function.
In Pass by Reference, function is called by directly passing the reference/address of the variable as the argument. Changing the argument inside the function affect the variable passed from outside the function.
example
##
Hoisting 变量提升
Hoisting is a JavaScript mechanism where variables and function declarations are moved to the top of their scope before code execution.
Execution Context
- Global execution context (GEC): This is the default execution context in which JS code start it’s execution when the file first loads in the browser.
- Functional execution context (FEC): Functional execution context is defined as the context created by the execution of code inside a function. Each function has its own execution context.
Execution context stack
- Execution context stack is a stack data structure to store all the execution stacks created while executing the JS code.
- Global execution context is present by default in execution context stack and it is at the bottom of the stack.
- While executing global execution context code, if JS engines finds a function call, it creates functional execution context of that function and pushes that function execution context on top of execution context stack.
- JS engine executes the function whose execution context is at the top of the execution context stack.
- Once all the code of the function is executed, JS engines pop’s out that function’s execution context and start’s executing the function which is below it.
JavaScript engine creates the execution context in the following two stages:
Creation phaseandExecution phase.
In creation phase, JS engine performs the following task:
- creates the
activation objector thevariable object:activation objectis a special object in JS which contain all the variables, function arguments and inner functions declarations information. - creates the
scope chain: Once theactivation objectgets created, JS engine initializes the scope chain which is a list of all thevariables objectsinside which the current function exists. This also includes thevariable objectofglobal execution context. Scope chain also contains the currentfunction variable object. - determines the value of
this: After thescope chain, JavaScript engine initialize the value of‘this’.
- creates the
In the execution phase, JS engines will again scan through the function to update the variable object with the values of the variables and will execute the code.